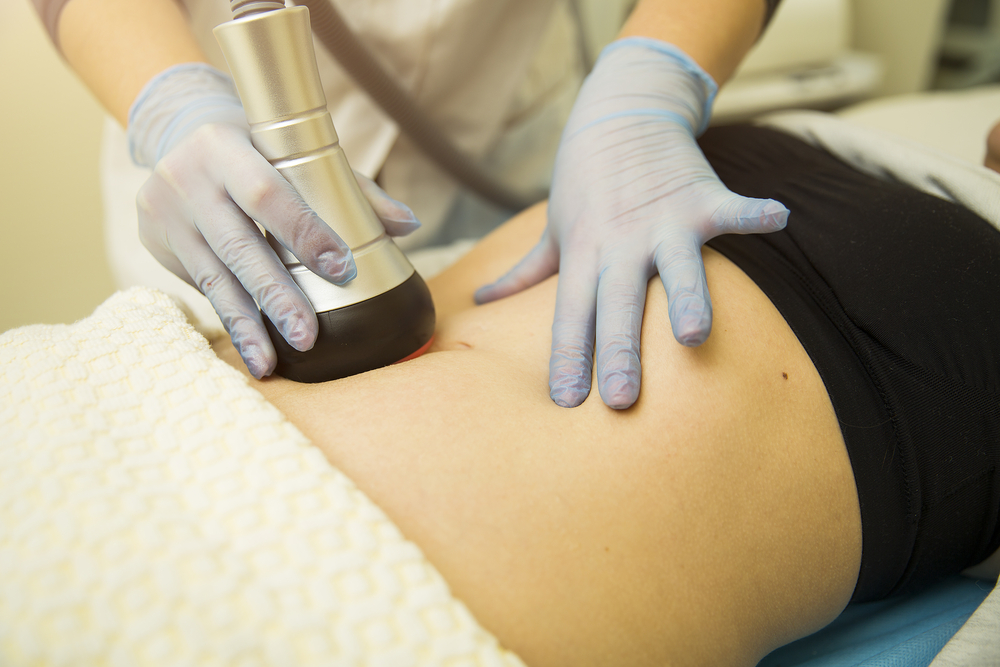
- Liposuction is the top cosmetic surgery in the United States, with some 400,000 procedures performed every year on various parts of the body.
- Laser liposuction is one of several relatively new technologies that are now offered as a way to replace or enhance this classic body contouring procedure.
- Laser liposuction might seem like a great option on the surface. However, many plastic surgeons warn that it often comes with serious consequences.
- Depending on the body area, laser liposuction can cost anywhere from $2,500 – $5,000.
For free consultation on Laser Liposuction services, register with us here now!
[wpforms id=”44645″ title=”false”]
What is laser liposuction?
Laser liposuction, sometimes called laser-assisted liposuction, laser lipoplasty, laser lipo, or laser lipolysis, is also known under various ‘brand’ names, like TriSculpt and Accusculpt.
Other popular brands include:
- SmartLipo
- SlimLipo
- SmoothLipo
- Lipotherme
- LipoLite
- CoolLipo
- ProLipo
- Airsculpt
Similar to traditional liposuction, laser lipo is performed under local anesthetic. “Laser lipo works by passing a very thin fiber optic cable under the skin carrying a laser beam which heats tissues to 900 degrees, thereby melting the fat,” explains Dr. Leonard Grossman, a plastic surgeon practicing in New York, NY.
Is laser liposuction effective?
When first studied and introduced in the early 1990s, laser liposuction treatment did not receive FDA-approval as there was no real benefit shown. In the early 2000s however, new lasers were introduced that subsequently gained FDA-approval.
Various studies indicate that laser is effective and does provide benefits in terms of reducing fat and tightening the skin. However, as plastic surgeon Dr. Michael Frederick of Palm Beach Gardens, FL warns, “there has never been a good study proving that the laser tightens the skin more than any other method of liposuction.”
A further review of current scientific literature seems to prove Frederick right, the general consensus being that there is no clinical advantage to laser liposuction over traditional liposuction procedures.
According to a study published in The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, several clinicians “have been reluctant to accept laser lipolysis, citing longer procedural times, increased risk of adverse reactions, and lack of evidence supporting superiority over traditional liposuction.”
Laser liposuction side effects and complications
Laser liposuction might seem like a great option on the surface. However, many plastic surgeons warn that it often comes with serious consequences.
Grossman explains, “where traditional lipo uses a vacuum attached to a thin cannula [tubing] to remove fat, laser lipo melts the fat through high temperatures. Because different tissues absorb heat differently, this results in uneven texture of subcutaneous fat and connective tissues.”
That’s only part of the problem: “It’s not just the uneven texture of the surface,” adds Grossman. “If this was just the fat that was left lumpy, it could be easily fixed, but it is not — it has literally charred tissues.”
“Imagine yourself throwing a mix of fat, muscle, tendons, and connective tissue on a frying pan,” says Grossman. “Each tissue will react differently to the high temperature. Some quicker than others will denature. Longer contact will result in a deep tissue burn or charring. These tissues take a long time to be cleaned up by the body.”
If the idea of charred fat doesn’t sound too appealing, the idea of third degree burns is even more horrifying. When skin burns occur from laser liposuction, “these are of the third degree and always leave disfiguring scars,” adds Grossman.
There is also a greater risk of infections with laser liposuction, while with traditional liposuction, infections and side effects are rare.
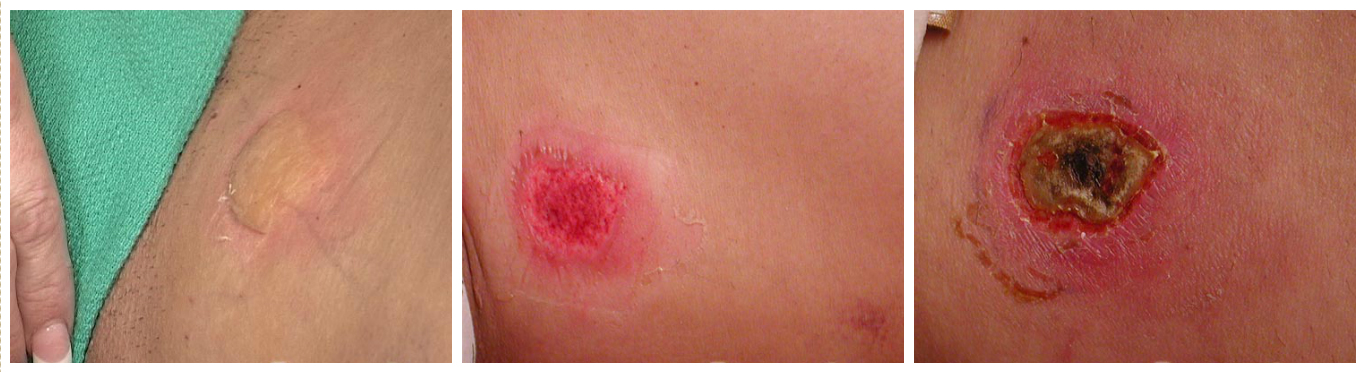
If you’re wondering how common these side effects and complications are, let us share some statistics.
Based on the current evidence available, approximately 1% of laser procedures result in complications, compared to traditional liposuction complication rates of less than 0.3%. Laser liposuction also has a 3.5% to 7.3% revision rate, meaning people frequently have to go back and have things fixed.
Grossman suggests that these figures are way too low, saying, “I personally would not recommend laser lipo to be used under any circumstances after the amount of complications that I have seen since the inception of the procedure in 2002 – 2003.”
Research from 2013 indicates that 89.5% of plastic surgeons use traditional liposuction, while only 10.5% use laser.
The important thing to be aware of is that roughly 40% of laser liposuction procedures are performed by noncore practitioners with very little surgical training. These include obstetricians, gynecologists, dermatologists, orthopedic surgeons, and family medicine physicians. While some may have advanced training, many are unskilled at performing this procedure.
Still, plastic surgeons may use laser in some instances. However, they are well versed in various types of surgical procedures and can offer the best alternatives. Just keep in mind that if you choose to have laser liposuction, your choice of provider will be critical, as the risks of complications increase when dealing with inexperienced operators.
Another important thing to consider is future procedures that you may need or want. As laser liposuction kills the blood vessels, this “can make it more risky to do a secondary abdominoplasty or tummy tuck, as now the normal blood supply has been disrupted,” says Frederick. As a patient, you may limit your future surgery options.
Grossman also warns that when complications occur from laser liposuction, you can expect an extended wait of two years before you can undergo any further surgery or revisions, otherwise you may risk further complications.
Additionally, it is often impossible to completely correct the problems that can arise from laser liposuction.
Save the fat
Dr. Ryan Welter of Regeneris Medical in North Attleboro, MA suggests another major drawback to laser liposuction that’s often overlooked — the fat can no longer be used for other purposes.
“Regenerative scientists have demonstrated that fat is a huge reservoir for stem cells, which can be exploited to treat a host of medical and cosmetic conditions,” says Welter. “Since there are other liposuction techniques that can salvage the fat, I recommend storing the fat — or better yet using it immediately.”
For instance, “fat transfers for facial rejuvenation are very popular and can have the same effects of Botox but last for years,” says Welter.
According to the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, fat grafting is becoming increasingly popular, especially for use on the face, buttocks, and breasts. The advantage of using your own fat is that you don’t run the risk of rejection and complications that can come with implants or artificial fillers.
Is laser liposuction better than traditional liposuction?
As a consumer, it’s important to be aware of the marketing tactics that may be used to promote laser liposuction as a better option.
You may hear that:
- Results are noticeable sooner
- It’s less invasive
- It’s more effective
- It has a faster recovery time
- It results in less blood loss
- It provides superior skin tightening
- It’s less painful
However, here are some facts to bear in mind:
- There is no evidence to show a clinically significant pain score difference between the two procedures.
- In terms of outcomes, no difference has been found in patient satisfaction between the two procedures.
- There is no difference in blood loss between the two procedures. As Frederick notes, standard liposuction only leads to minimal blood loss. Typically, under a 1% of blood is lost during the procedure.
- While laser liposuction is often suggested as a ‘non invasive’ procedure, this isn’t entirely true. “Laser lipo is traditional liposuction. The laser lipo still uses a cannula to remove the fat,” says Frederick. “They just add a laser to the process.”
- Laser liposuction is less time-efficient than traditional liposuction .
- Laser liposuction results in more side effects and complications than traditional liposuction.
Overall, the overwhelming consensus of all the scientific research conducted so far shows that there are no advantages to laser liposuction over traditional liposuction procedures.
How much does laser liposuction cost?
Depending on the body area, laser liposuction can cost anywhere from $2,500 – $5,000.
Does Laser Liposuction Work?
Highlights from Scientific Studies
Early on, laser liposuction failed to gain FDA approval because scientific studies of the technology showed no particular benefit. By the early 2000s lasers had begun to gain approval, as studies showed that they can be very effective for reducing fat and tightening the skin
However, no study has yet proved that lasers provide tightening that is superior to other methods of liposuction.
In fact, a review of scientific studies seems to show that laser liposuction does not offer any clear clinical advantage to over traditional liposuction techniques.
An influential study published by The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology cited several clinicians as being reluctant to accept laser liposuction due to the duration of the procedure, the risk of adverse reactions, and the scarcity of evidence to show that it is more effective than traditional liposuction.
The same study found that while the safety of laser liposuction is well documented, and skin tightening is a significant advantage of this method, some disadvantages still exist:
- On its own, laser liposuction may be insufficient for proper correction.
- Many clinicians believe laser liposuction should be viewed as complementary to traditional liposuction, as opposed to a standalone treatment.
- An increased procedure time, since many surgeons use this treatment as an adjunct to traditional liposuction.
- The risk of thermal injury.
- The flexibility and thinness of the cannula used in laser liposuction may make it difficult for the surgeon to discern the depth of tissues, which could have an impact on the final results.